
Introduction
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) provide a comprehensive framework for the preparation and presentation of financial statements globally. At the core of this framework is IAS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements, which sets out the overall requirements for how financial statements should be structured and what they must contain.
Key Components of a Financial Statement under IAS 1
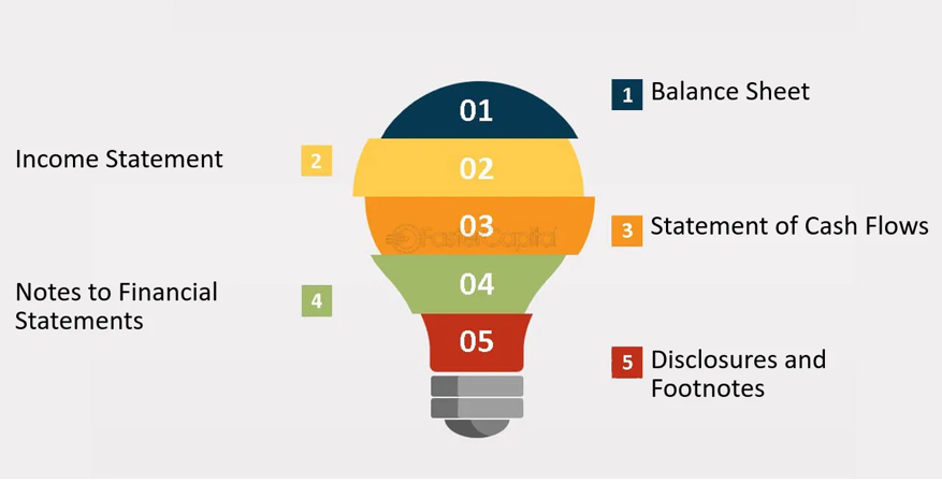
These statements must faithfully represent the financial position, performance, and cash flows of the entity in accordance with IFRS definitions and recognition criteria. Companies must make an explicit and unreserved statement of IFRS compliance.
IAS 1 also establishes key principles such as the going concern assumption, accrual basis of accounting, and current/non-current distinction on the balance sheet. It provides guidance on the structure, content, and order of the financial statement components.
Updates from the issue of IFRS 18
On the 9th of April 2024, IAS 1 will be superseded by the new IFRS 18; Presentation and Disclosure in Financial Statements standard. IFRS 18 is effective for annual reporting periods beginning on or after 1st January 2027, but companies can choose to apply it earlier. IFRS 18 builds on the foundation of IAS 1 but introduces several enhancements:
- Categorizing items in the statement of profit or loss as operating, investing or financing
- Requiring additional profit subtotals to be presented
- Distinguishing between integral and non-integral associates and joint ventures
- Removing the choice of how to present cash flows from dividends and interest
- Requiring additional disclosure about unusual items
- Providing disclosure of management performance measures
These changes are aimed at improving the transparency, comparability and usefulness of financial reporting for investors and other stakeholders. (https://www.iasplus.com/en/standards/ifrs/ifrs-18)
General requirements for Financial Statements
The objective of financial statements is to provide financial information about a reporting entity’s assets, liabilities, equity, income, and expenses that is useful to users of financial statements in assessing the prospects for future net cash inflows to the entity and in assessing management’s stewardship of the entity’s economic resources. [IFRS 18.9]
Key stakeholders who rely on IFRS financial statements include:
- Investors – to assess the entity’s ability to generate future cash flows and returns
- Lenders – to evaluate the entity’s creditworthiness and ability to repay loans
- Suppliers and other trade creditors – to determine payment terms and collection prospects
- Regulators – to monitor compliance with laws and regulations
- Employees – to assess the entity’s stability and profitability
The comprehensive disclosures required by IFRS, including the notes to the financial statements, are crucial in enabling these stakeholders to make informed decisions.
Overall, the IFRS framework for financial statement preparation ensures that companies worldwide produce high-quality, transparent and comparable financial information. The upcoming IFRS 18 standard will further enhance the relevance and decision-usefulness of this information for all users.
